Plateaus:
Plateau is an extensive area of flat upland. They are storehouse of Mineral deposits. Based on their geographical location they are of following types:
1. Intermontane plateau: Partly or fully enclosed b/w mountain ranges. e.g. Tibetan plateau
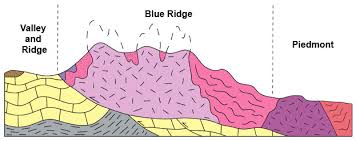
2. Piedmont plateau: Located on foot of mountain and locked on other side by either a plain on an ocean. They once had the height of mountain but reduced to mountain foot by erosion. e.g. Malwa plateau.
3. Continental plateau: They are formed by continental upliftment or spread of lava sheet. e.g. Plateau of Maharashtra.
4. Volcanic plateau: They are formed by volcanic activity. e.g. Deccan trap
5. Dissected plateau: Their relief is sharp because of erosion.

Plains:
They are the simplest landforms. They have a very gentle slope and minimum relief. They are most populated landforms. e.g. Indo-gangetic plains.
.jpg)
Plateau is an extensive area of flat upland. They are storehouse of Mineral deposits. Based on their geographical location they are of following types:
1. Intermontane plateau: Partly or fully enclosed b/w mountain ranges. e.g. Tibetan plateau
2. Piedmont plateau: Located on foot of mountain and locked on other side by either a plain on an ocean. They once had the height of mountain but reduced to mountain foot by erosion. e.g. Malwa plateau.
3. Continental plateau: They are formed by continental upliftment or spread of lava sheet. e.g. Plateau of Maharashtra.
4. Volcanic plateau: They are formed by volcanic activity. e.g. Deccan trap
5. Dissected plateau: Their relief is sharp because of erosion.
Plains:
They are the simplest landforms. They have a very gentle slope and minimum relief. They are most populated landforms. e.g. Indo-gangetic plains.
.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment