The Earth have following layers:
1. Crust
2. Mantle
3. Core
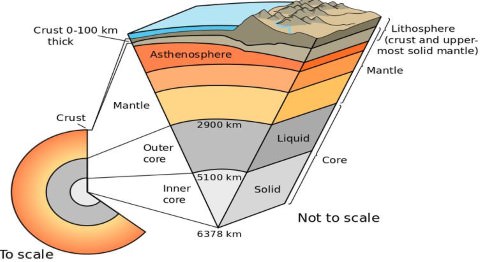
Crust is the uppermost layer of the Earth. Its total thickness varies from 30-50 km. Its main constituents are Silicon and Aluminium and hence also called SIAL. There are 2 types of Crust- Continental and Oceanic. Continental Crust is thicker than Oceanic Crust. Thickness of Continental crust varies from 50-70 Km and that of Oceanic crust varies from 5-30 Km. Crust is further divided into Upper and Inner Crust. The discontinuity b/w Upper and Inner crust is known as Conard discontinuity.
Below the Crust, the Mantle extends to a depth of 2900 km. The main constituents of Mantle are Silicon and Magnesium and hence it is also called SIMA. It is further divided into Upper and lower mantle. Together the Crust and upper part of Mantle which is in solid state, form 'Lithosphere'. Lithosphere floats over a highly viscous substance called Asthenosphere. Asthenosphere is main source of magma. The discontinuity b/w Crust and Upper mantle is called Moho discontinuity. The discontinuity b/w Upper mantle and lower mantle is called Repetti Discontinuity.
The innermost part is called Core. It is made of mainly Iron(Fe) and Nickel(Ni) and hence also called NiFe. It is further divided into Outer core and Inner Core. The outer core is in liquid or semi-liquid state because of extremely high temperature. The inner core is in solid state. The reason for it being in solid state despite so high temperature is that the pressure in this region also becomes very high. This increased pressure increases the melting point of rocks and hence they cannot by melted. So the inner core remains in solid state. The discontinuity b/w lower mantle and core is called Guttenberg discontinuity. The discontinuity b/w outer core and inner core is called Lehmann discontinuity.
Trick to remember Discontinuities:
Starting from the top the layers we have are-
Upper crust, Lower crust, Upper Mantle, Lower Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core
So the discontinuities can be remembered by following line-
CM of Rajasthan is GehLot.
Where C is Conard, M is Moho, R is Repetti, G is Guttenberg and L is Lehmann.

Comments
Post a Comment