NOTE: Magma is molten rock below Earth's crust. Lava is magma that has reached the earth's surface.
A mountain is a large landform that stretches above the surrounding land in a limited area, usually in the form of a peak. Types of mountains:
A mountain is a large landform that stretches above the surrounding land in a limited area, usually in the form of a peak. Types of mountains:
1. Fold Mountains:
They are formed when two continental plates or one continental and one oceanic plate move towards each other at a convergent plate boundary. When the two plates collide the sedimentary deposits along the edges of Continental plates are forced to fold and hence folded mountains are formed. e.g. Himalyas.
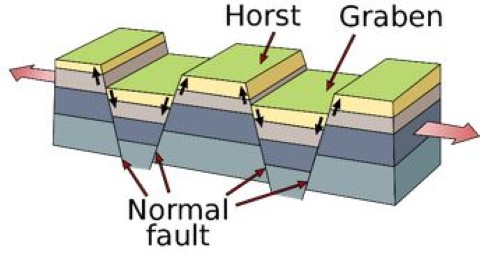
2. Block mountains:
They are formed due to faulting. They are not true mountains as they are formed by differential settlement of land mass. There is no actual upliftment taking place as in case of fold mountains. Middle part of any land mass gets lowered resulting into relatively raising of adjoining landmasses or Lowering of landmasses on either sides resulting into relatively raising of middle landmass. Block mountains are surrounded by faults on side of rift valleys or grabens. The uplifted part is called Horst and the depression is called Graben. e.g. Great African Rift valley.

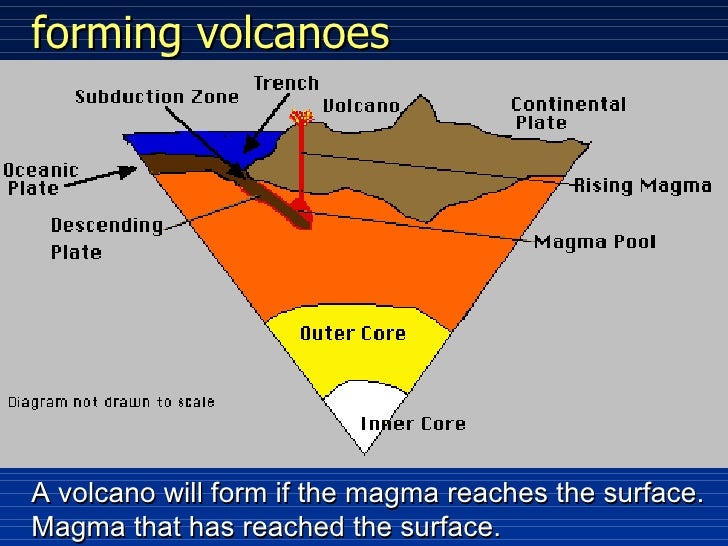
3. Volcanic mountains:
When a continental and an oceanic plates move towards each other at a convergent plate boundary, the oceanic plate subduct beneath continental plate because oceanic plate is denser. Due to high temperature below continental crust the oceanic plate melts and turns into magma. This magma is forced to come to the surface. When this magma reaches the earth's surface it cools down it formsrocks and eventually form Volcanic mountains. e.g. Mt. Fiji in Japan.

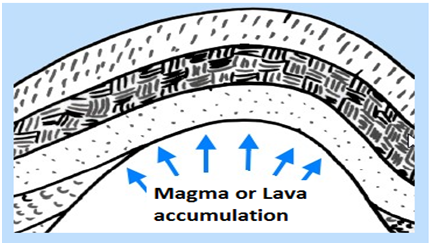
4. Dome mountains:
Formed when molten rock or magma pushes its way up under earth's crust. The magma does not erupts to the earth's surface but just pushes up the overlaying rock layers. e.g. Adirondack mountains of Australia.



5. Residual mountains:
They are formed from already existing mountains which are reduced by agents of denudation like water, air, ice etc. e.g. Mt. Monadnock in USA.


Comments
Post a Comment