The Solar System is a gravitationally bound system comprising Sun, planets, asteroids, meteoroids, kuidper belt etc. It was formed about 4.6 Billion Years ago from gravitational collapse of giant interstellar molecular cloud.
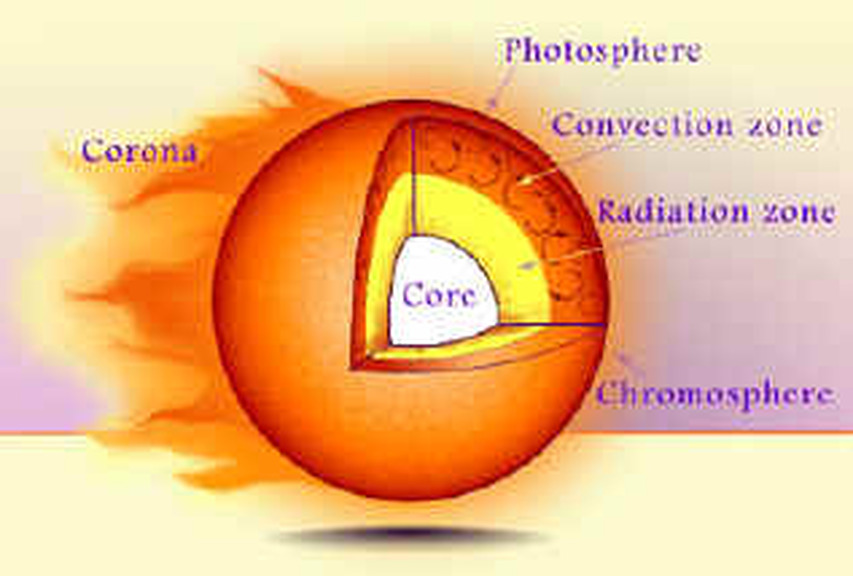
Internal Structure of Sun:
1. Photosphere: The visible part of the sun. It comprises 3 regions:
i. Core: The innermost part of the sun. Nuclear Fusion reaction takes place in this region. Temperature and pressure are extremely high.
ii. Radioactive Zone: Above the core and emits radiation.
iii. Convective Zone: Photons produced in the core make their way to the surface of the sun through this Zone.
2. Chromosphere: Red colored surface above photosphere. The temperature increases as the distance increases from the centre. This layer is visible only during Solar Eclipse.
3. Corona: This layer is also visible only during Solar Eclipse. Also emits X ray radiation.
Solar Phenomenon:
1. Solar wind: Streams of charged particles released from upper atmosphere of the Sun.
2. Solar flares: Brief eruption of high energy radiation from the surface of Sun. It is associated with sunspots and causes radio and magnetic disturbances in earth.
3. Sunspots: Temporary phenomenon on the surface of the Sun. Appear as dark spots on the sun and are comparatively cooler. No radiation is emitted from these regions.
4. Aurora: Caused when earth's magnetic field interact with solar wind forming colorful lights in the sky of North and South poles.
Some important celestial bodies:
1. Asteroids: A celestial body made of rocks and metals with diameter greater than 10m. They orbit around the Sun and are mainly present between Mars and Jupiter.
2. Meteoroid: A small rock in solar system with size ranging b/w that of a dust to 10 m diameter.
3. Meteor: When a meteoroid enters the earth's atmosphere it is called Meteor. Due to friction by Earth's atmosphere it burns up in the mid way and do not reach earth's surface. During night they can be seen as a streak of light and also known as shooting stars.
4. Meteorite: When a meteoroid hits the earth's surface it is called Meteorite.
5. Fireball: A very bright meteor(brighter than Venus)
6. Bolide: A fireball which explodes during its atmospheric flight.
7. Comet: These are smaller celestial bodies composed of ice, rocks and dust. When they comes near to sun the ice melts and turn into gas. Due to this melting process the dust and debris forms a trail behind the comet. This tail can be seen in night as bright, quickly moving light.
Some important celestial bodies:
1. Asteroids: A celestial body made of rocks and metals with diameter greater than 10m. They orbit around the Sun and are mainly present between Mars and Jupiter.
2. Meteoroid: A small rock in solar system with size ranging b/w that of a dust to 10 m diameter.
3. Meteor: When a meteoroid enters the earth's atmosphere it is called Meteor. Due to friction by Earth's atmosphere it burns up in the mid way and do not reach earth's surface. During night they can be seen as a streak of light and also known as shooting stars.
4. Meteorite: When a meteoroid hits the earth's surface it is called Meteorite.
5. Fireball: A very bright meteor(brighter than Venus)
6. Bolide: A fireball which explodes during its atmospheric flight.
7. Comet: These are smaller celestial bodies composed of ice, rocks and dust. When they comes near to sun the ice melts and turn into gas. Due to this melting process the dust and debris forms a trail behind the comet. This tail can be seen in night as bright, quickly moving light.

Comments
Post a Comment